Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires? This isn’t just about bigger flames; it’s about a whole system shift. Rising temperatures are extending fire seasons, creating drier, more flammable landscapes, and intensifying the fires themselves. We’ll explore how climate change is impacting everything from the length of fire seasons to the effectiveness of firefighting efforts, painting a clearer picture of this increasingly complex problem.
We’ll delve into the specifics: how earlier snowmelt and prolonged heat contribute to longer fire seasons, how climate change alters vegetation making it prime fuel, and how it influences ignition sources and fire behavior. Think faster-spreading fires, more intense flames, and challenges for firefighters trying to control the blazes. Get ready to understand the interconnectedness of climate change and California’s wildfire crisis.
The Impact of Climate Change on California’s Wildfire Season Length
California’s wildfire season is significantly lengthening due to climate change. Rising temperatures and earlier snowmelt create longer periods of dry, hot conditions, extending the window of opportunity for wildfires to ignite and spread.
Extended Wildfire Seasons in California
Data from the past few decades reveals a clear trend of lengthening wildfire seasons. For example, the average wildfire season in Southern California has increased by approximately two months since the 1970s. This prolonged fire season increases the cumulative risk of large, destructive wildfires. Longer, hotter, and drier conditions increase the chances of wildfires starting and growing larger, as well as making them more difficult to control.
Impact of Longer Fire Seasons
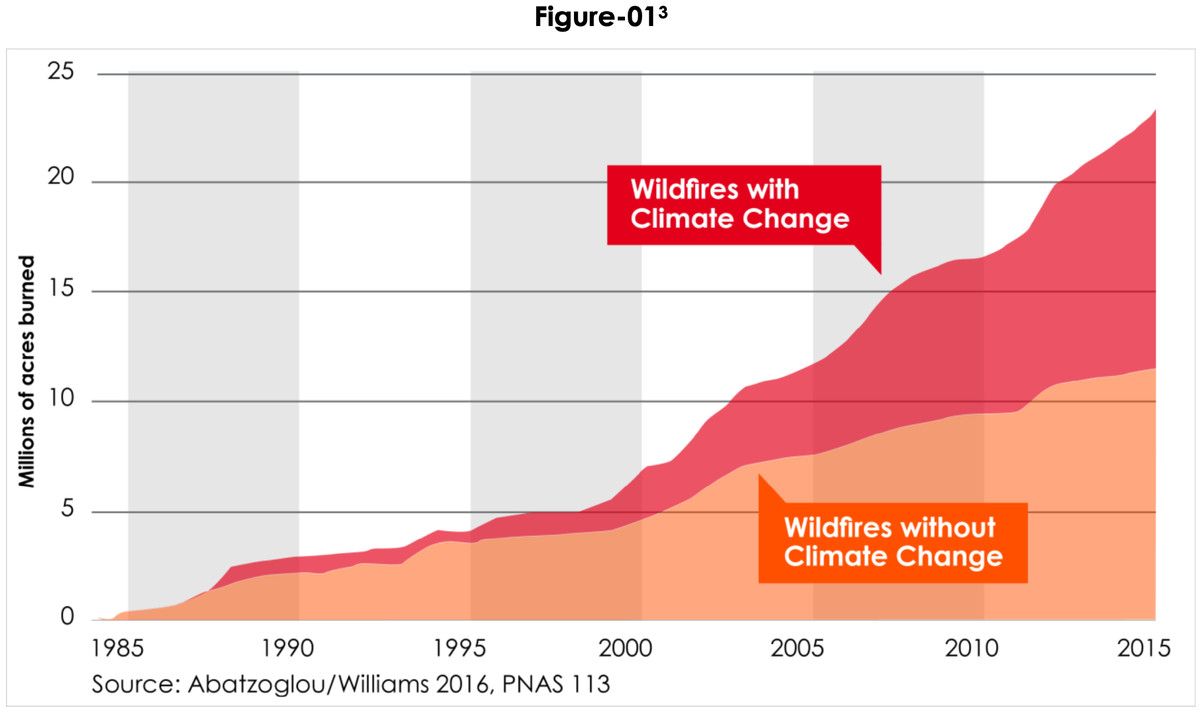
The consequences of longer fire seasons are far-reaching. Increased wildfire activity leads to greater property damage, loss of life, and significant environmental degradation. The longer the season, the more resources are needed for prevention, suppression, and recovery efforts, straining budgets and putting pressure on emergency responders. The cumulative effect of successive fire seasons without adequate recovery time leads to landscape-level changes, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Average Wildfire Season Lengths Across California Regions
| Year | Region | Start Date | End Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Southern California | May 15 | November 15 |
| 2020 | Northern California | June 1 | October 1 |
| 2010 | Southern California | June 1 | October 1 |
| 2010 | Northern California | June 15 | September 15 |
Climate Change and Fuel Conditions
Climate change significantly alters the fuel conditions that support wildfires. Increased drought frequency and intensity lead to drier vegetation, making it more susceptible to ignition and rapid spread. Changes in vegetation patterns also influence fuel loads, increasing the risk of intense wildfires.
Increased Drought and Flammable Vegetation, Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires

More frequent and intense droughts directly contribute to the increased flammability of vegetation. Prolonged periods without sufficient rainfall lead to dry grasses, shrubs, and trees, creating ideal conditions for fire ignition and rapid spread. This effect is amplified in areas experiencing hotter temperatures, further drying out the vegetation.
Climate Change Impacts on Vegetation Growth and Density
Climate change affects the types of vegetation that thrive in various regions. For instance, the expansion of drier, more flammable plant species into areas previously dominated by more moisture-tolerant vegetation increases overall fuel loads and the risk of large wildfires. Changes in forest density, such as increased tree mortality due to drought or pests, also contribute to increased fuel availability.
Flammability of Different Vegetation Types
Different plant species have varying flammability characteristics. For example, chaparral, a common vegetation type in California, is highly flammable, especially during drought conditions. Coniferous forests, while less flammable in moist conditions, become highly combustible when dry. Climate change alters the distribution and abundance of these vegetation types, influencing the overall fire risk.
Specific Ways Climate Change Affects Fuel Conditions
- Increased dryness of vegetation due to prolonged drought.
- Shift in vegetation types towards more flammable species.
- Increased density of underbrush and deadwood.
- Reduced soil moisture content.
- Higher overall biomass accumulation.
Climate Change and Ignition Sources
Climate change influences the frequency and intensity of several ignition sources, increasing the likelihood of wildfires. Changes in weather patterns lead to more frequent lightning strikes, while stronger winds contribute to faster fire spread. Extreme heat also increases human activity in areas prone to wildfires, leading to accidental ignitions.
Increased Lightning Strikes
Warmer temperatures and altered atmospheric conditions can lead to more frequent and intense thunderstorms, resulting in a higher number of lightning strikes. These strikes can ignite dry vegetation, especially in remote areas where human intervention is limited, leading to the initiation of wildfires.
Increased Wind Events and Fire Spread
Climate change is associated with an increased frequency and intensity of strong winds. These winds can rapidly spread wildfires over vast distances, making them more difficult to control and increasing the area affected. Strong winds also increase the intensity of fires, leading to more extreme fire behavior.
Extreme Heat and Human Activity
Extreme heat increases human activity in outdoor areas, potentially leading to more accidental ignitions. Increased recreational activities, combined with higher temperatures and drier conditions, elevate the risk of human-caused wildfires.
Ignition Sources and Climate Change Correlation
| Ignition Source | Climate Change Factor | Frequency | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lightning | Increased thunderstorm activity | Increased | Increased wildfire ignitions, particularly in remote areas |
| Human activity | Increased heat and dry conditions | Potentially increased | Increased accidental ignitions due to human carelessness |
| Equipment malfunction | Increased use of equipment in dry conditions | Potentially increased | Increased risk of equipment-related ignitions |
The Role of Climate Change in Fire Behavior
Higher temperatures and lower humidity, both consequences of climate change, dramatically alter wildfire behavior. These conditions contribute to faster fire spread, increased intensity, and a greater likelihood of extreme fire behavior such as crown fires.
Faster Fire Spread and Increased Intensity
Higher temperatures dry out fuels, making them more readily combustible. Lower humidity further reduces the moisture content of vegetation, increasing flammability. These combined factors lead to significantly faster fire spread and increased intensity, making wildfires more difficult to control.
Influence of Climate Change on Fire Behavior
Climate change is linked to an increase in crown fires – fires that spread through the canopies of trees – and extreme fire behavior, characterized by rapid and unpredictable fire spread, intense heat release, and spotting (the creation of new fire starts ahead of the main fire front). These extreme fire events cause significant damage and pose significant challenges to suppression efforts.
Impact of Climate Change on Fire Size and Severity
Data indicates a clear trend of increasing fire size and severity in California in recent decades. This is partly attributable to the increased frequency and intensity of extreme fire behavior driven by climate change.
Wildfire Progression Under Different Conditions

Under normal conditions, a wildfire might spread relatively slowly, with flames reaching a moderate height. Under conditions exacerbated by climate change, however, the fire could spread rapidly, with significantly higher flames and increased intensity, potentially resulting in a crown fire.
Okay, so California’s burning – a huge problem linked to climate change and its impact on drier conditions and more intense wildfires. It’s a stark reminder of our shared challenges, even as we see moments of unity like All five living US presidents pictured together at funeral of Jimmy , which highlights the importance of collaboration. Ultimately, tackling climate change requires that same level of global cooperation to prevent future devastating fire seasons.
Climate Change and Fire Suppression Efforts: Climate Change: What Role Is It Playing In The California Fires
Climate change presents significant challenges to fire suppression efforts. Changing weather patterns, including stronger winds and increased temperatures, make it more difficult to contain and control wildfires. These conditions also increase the risk to firefighters and the effectiveness of traditional suppression strategies.
Challenges to Fire Suppression
Increased temperatures and lower humidity create more challenging conditions for firefighters. Extreme heat can lead to exhaustion and heatstroke, while strong winds make it difficult to control fire spread and increase the danger to firefighting personnel. The longer fire seasons also put a strain on resources and personnel.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drought and extreme heat. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes, amidst the chaos, you might find yourself needing a distraction; for example, check out this article about Denise Richards’ 2022 Road Rage Gun Incident: What to Know if you need a break from the grim realities of climate change.
Then, remember to get back to thinking about how we can all work together to mitigate the effects of climate change on our environment and prevent future devastating wildfires.
Effectiveness of Fire Suppression Strategies
The effectiveness of fire suppression strategies, such as controlled burns and deploying firefighters, is reduced under extreme weather conditions. Strong winds can quickly overwhelm fire lines, while high temperatures and low humidity can increase the intensity of the fire, making containment efforts more difficult.
Wildfire Suppression and Climate Change Impacts
A flowchart illustrating the steps involved in wildfire suppression and how climate change affects each step would show how each stage, from initial detection and response to containment and mop-up, is impacted by factors like increased fire spread rate, extreme fire behavior, and limited resource availability due to longer fire seasons and increased demand.
Last Word
The link between climate change and California’s devastating wildfires is undeniable. From longer fire seasons and increased fuel loads to intensified fire behavior and hampered suppression efforts, the impacts are far-reaching and severe. Understanding this connection is crucial not only for mitigating future risks but also for developing more effective strategies to protect lives, property, and the state’s precious natural resources.
The challenge is significant, but by acknowledging the role of climate change, we can begin to build a more resilient future.
California’s increasingly intense wildfires are a stark reminder of climate change’s impact. Drier conditions and higher temperatures create a perfect storm for devastating blazes, as we’ve seen time and time again. To understand the human cost, check out this account of the Palisades Fire: Actor Steve Guttenberg recounts his Palisades Fire experience. His story highlights the urgent need to address climate change and mitigate the risks of future wildfires in the state.
FAQ Corner
What specific human activities exacerbate climate change and thus worsen California fires?
Burning fossil fuels (cars, power plants) releases greenhouse gases, trapping heat and driving climate change. Deforestation reduces the planet’s ability to absorb CO2. Increased urban sprawl increases the interface between human development and wildlands, leading to more ignition sources.
Are there specific types of vegetation more susceptible to fire due to climate change?
Yes, drought conditions fueled by climate change make many plants more flammable. For example, chaparral, common in California, becomes incredibly dry and easily ignited under prolonged drought.
How does climate change affect the effectiveness of firebreaks?
Intense winds driven by climate change can easily overcome traditional firebreaks, making them less effective at containing fires.
What role does air quality play in the context of California wildfires and climate change?
Wildfires release massive amounts of smoke and pollutants into the air, causing significant respiratory problems. Climate change worsens air quality by creating conditions that favor larger and more intense fires.
